Amunet Goddess
Goddess Amonet: Protector and Primordial Deity
Mythical Essence of Amonet
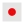
Amonet, revered as "the Hidden One" and "the mother who is father embodies the north wind and the giver of life in Egyptian mythology. Her Egyptian name is Amenet, and she was often depicted as a serpent or a snake-headed woman wearing the Red Crown of Lower Egypt at Thebes, and sometimes as a frog-headed woman at Hermopolis. She also took the form of a cow
Role in Egyptian Mythology
Amonet played a pivotal role as the tutelary deity of pharaohs during their coronation ceremonies often accompanied by the god Min. In the cosmogony of Thoth, she was considered the partner of Amon, though her importance waned with the rise of Mut who later supplanted her as the wife of Amon, especially as the cult of Osiris gained prominence. Nevertheless, Amonet and Amon were crucial figures in the Hermopolitan Ogdoad, one of the ancient Egyptian groups of eight primordial deities.
Significance and Worship
The theology of Hermopolis, which predates the Theban triad of the New Kingdom established Amonet and Amon as foundational divine entities. Their influence persisted through various Egyptian dynasties, with a resurgence of reverence during the late period (25th to 31st dynasties). Amonet's cult flourished during the Middle and New Kingdoms, with significant temples dedicated to her in Hermopolis, Karnak (alongside Amon and Mut) and Luxor (under the form of Opet)
Cult of the Goddess
Priests dedicated to Amonet's specific cult were established as early as the XVIII Dynasty, serving as prophets of Ammonet. Her worship spanned across Egypt, reflecting her enduring appeal and significance as a divine protector and creator.
Embark on an Egyptian Journey
Unveil the mysteries of ancient Egypt by exploring the pharaonic era through our Egypt tours. Experience a Day Tour to the Egyptian Museum and a Safari tour around the Pyramids discovering the rich history and cultural heritage of this ancient land
 English
English
 Español
Español
 Chinese
Chinese
 français
français
 português
português
 Italian
Italian
 Russian
Russian
 Czech
Czech
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Japanese
Japanese
-webp.jpg)








